

Any client application that uses a database must establish a connection to that database before any work can be done. The connection forms a channel through which all activity from the client application takes place. For example, your user ID determines permissions to perform actions on the database—and the database server has your user ID because it is part of the request to establish a connection.
When a user connects to a database, the database server assigns the connection a unique connection ID. For each new connection to the database server, the server increments the connection ID value by 1. These connection IDs are logged in the -z server output. The connection ID can be used to filter request logging information, identify which connection has a lock on the database, or track the total number of connections to a server since it started and the order in which those connections were made.
See Request logging and How locking works.
To establish a connection, the client application calls functions in one of the SQL Anywhere interfaces. SQL Anywhere provides the following interfaces:
| Interface | Details |
|---|---|
| ODBC | |
| OLE DB | Connecting to a database using OLE DB |
| ADO.NET | Connecting to a database |
| Embedded SQL | SQL Anywhere Embedded SQL |
| Sybase Open Client | |
| iAnywhere JDBC driver | |
| jConnect JDBC driver |
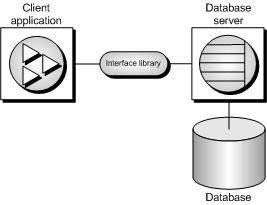
The interface uses connection information included in the call from the client application, perhaps together with information held in a data source, the SQLCONNECT environment variable, or the server address cache, to locate and connect to a server running the required database. The following figure is a simplified representation of the pieces involved.
The following table identifies where you can find answers to questions.
| If you want... | Consider reading... |
|---|---|
| An overview of connecting from Sybase Central or Interactive SQL (including a description of the drivers involved) | Connecting from Sybase Central, Interactive SQL, or the SQL Anywhere Console utility |
| Some examples to get started quickly, including Sybase Central and Interactive SQL scenarios | Simple connection examples |
| To learn about data sources | Working with ODBC data sources |
| To learn what connection parameters are available | Connection parameters |
| To see an in-depth description of how connections are established | Troubleshooting connections |
| To learn about network-specific connection issues | Client/Server Communications |
| To learn about character set issues affecting connections | Connection strings and character sets |
| To learn about connecting through a firewall | Connecting across a firewall |
How connection parameters work
Connection parameters passed as connection strings
Saving connection parameters in ODBC data sources